In the dynamic realm of electronics manufacturing, the terms PCB and PCBA are frequently encountered. Although sometimes used interchangeably, they represent distinct yet sequential stages in the creation of functional electronic devices. Grasping the PCB OR PCBA difference is vital for professionals and enthusiasts alike involved in electronics design, production, or sourcing. This article aims to clearly delineate these terms, illuminating their individual roles and their interconnected relationship.
What is a PCB? The Foundation of Electronic Circuits
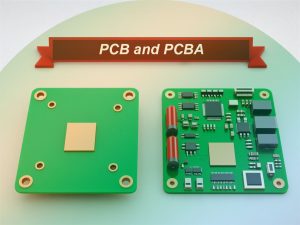
At its core, a Printed Circuit Board (PCB) is a non-conductive substrate, typically crafted from materials like fiberglass, epoxy composites, or laminates. Its primary role is to provide both mechanical support and electrical pathways for electronic components. The PCB features intricate conductive tracks, known as traces, etched onto its surface or within its internal layers. These traces serve as the highways for signals and power distribution between various components. Think of a PCB as the foundational wiring infrastructure of an electronic system – a sophisticated, albeit unpopulated, connection platform.
What is a PCBA? The Functional Electronic Assembly
A Printed Circuit Board Assembly (PCBA) represents the subsequent and crucial step in the electronics manufacturing process. A PCBA is essentially a PCB that has undergone the process of component population. This involves meticulously mounting and soldering electronic components – such as resistors, capacitors, integrated circuits (ICs), diodes, transistors, and connectors – onto the designated pads and through-holes of the bare PCB. The resulting PCBA is a fully functional electronic circuit board, ready for integration into a final electronic product.
Key Differences Summarized: Bare Board vs. Populated Board
The fundamental PCB OR PCBA difference boils down to the presence of electronic components. A PCB is a blank, etched board with conductive pathways, prepared to receive components. Conversely, a PCBA is the outcome of the PCB assembly process, where components have been attached and soldered, transforming it into an active electronic module capable of performing specific functions.
Analogies for Clarity: From Blueprint to Functional Unit
To further clarify the distinction, consider a construction analogy:
- PCB: The Foundation and Wiring. The PCB is akin to the foundation of a building and the pre-installed electrical wiring within its walls. It provides the structural support and the basic pathways for electrical connections.
- PCBA: The Fully Furnished Building. The PCBA is like the completed building with all the necessary appliances, light fixtures, and electrical outlets installed and fully connected. It’s the functional living or working space.
Why Understanding the PCB OR PCBA Difference Matters
Comprehending the distinction between a PCB and a PCBA holds significant importance across various aspects of the electronics industry:
- Design Phase: Electronic engineers design the circuit schematics and translate them into precise PCB layouts, dictating component placement and trace routing. This design serves as the blueprint for both the bare PCB and the eventual PCBA.
- Manufacturing Processes: Specialized PCB manufacturers produce the unpopulated circuit boards based on the design specifications. Subsequently, PCBA manufacturers take these bare PCBs and perform the assembly process, populating them with the required electronic components through automated and manual soldering techniques.
- Procurement and Sourcing: When acquiring electronic boards, clearly specifying whether you require bare PCBs or fully assembled PCBAs is crucial for accurate pricing, lead times, and supplier communication.
- Troubleshooting and Repair: In diagnosing malfunctions within electronic devices, distinguishing between potential issues residing in the PCB’s conductive layers or within specific components on the PCBA is essential for efficient fault isolation and repair.
Conclusion: Recognizing the Distinct Stages of Electronic Board Production
In conclusion, while the terms PCB and PCBA are intrinsically linked within the electronics manufacturing ecosystem, they denote distinct stages of production. The PCB represents the foundational, component-free circuit board, whereas the PCBA signifies the functional assembly resulting from the integration of electronic components onto the PCB. A clear understanding of this PCB OR PCBA difference is paramount for effective communication, streamlined processes, and successful outcomes in the electronics industry.
